What Muscles Does Jump Rope Work? Benefits of Exercise
What Muscles Does Jump Rope Work
Jump rope is a fantastic full-body workout that engages a surprising number of muscles! Here's a breakdown of the primary muscle groups you'll be working with:
Lower Body:
- Calves: The stars of the show! Jumping repeatedly strengthens and tones your calves, improving power and agility.
- Quads and hamstrings: These powerhouse muscles propel you off the ground with each jump, building strength and endurance.
- Glutes: Jumping activates your glutes, improving their shape and contributing to overall lower body power.
Core:
- Abs and obliques: Maintaining a stable core is crucial for proper jump rope form, engaging your abs and obliques for better balance and coordination.
Upper Body:
- Shoulders and back: Swinging the rope and maintaining an upright posture work your shoulders and back muscles, improving stability and posture.
- Forearms and biceps: Gripping and controlling the rope engages your forearms and biceps, building strength and endurance.
Benefits of Jump Rope Exercise
Jump rope exercise offers a wide array of benefits for both physical and mental health.Cardiovascular Benefits
Jumping rope elevates the heart rate, making it an excellent cardiovascular workout. It strengthens the heart and improves blood circulation, leading to a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.Weight Loss and Fat Burning
Jump rope exercise is highly effective for burning calories and shedding excess body fat. It engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, resulting in increased calorie expenditure and accelerated fat loss.Improved Coordination and Agility
The rhythmic nature of jumping rope enhances coordination, balance, and agility. It requires precise timing and synchronization between the hands and feet, improving overall motor skills.Increased Bone Density
Jumping rope is considered a weight-bearing exercise, which helps increase bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. It strengthens bones and joints, promoting overall skeletal health. For more interesting information visit our website urbansoutfitter.comMuscles Targeted by Jump Rope Exercise
Jump rope exercise primarily targets the muscles of the lower body, including the calves, quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Additionally, it engages the core muscles and the muscles of the upper body, albeit to a lesser extent.Primary Muscles Engaged
The primary muscles worked during jump rope exercise include:- Calves: Responsible for jumping and absorbing impact.
- Quadriceps: Extend the knee during each jump.
- Hamstrings: Flex the knee and extend the hip during each jump.
- Glutes: Stabilize the pelvis and support the body's weight.
Secondary Muscles Involved
In addition to the primary muscles, jump rope exercise also engages secondary muscles, including:- Abdominals: Contract to stabilize the torso and maintain proper posture.
- Back Muscles: Assist in maintaining an upright position and stabilizing the spine.
- Shoulders and Arms: Contract to control the movement of the rope and assist in generating momentum.
Detailed Look at Muscles Worked by Jump Rope
Let's take a closer look at the specific muscles targeted by jump rope exercise:Lower Body Muscles
Calves
The calves play a crucial role in jumping rope, as they are responsible for propelling the body off the ground and absorbing the impact upon landing. Continuous jumping strengthens the calf muscles, leading to improved power and endurance.Quadriceps and Hamstrings
The quadriceps and hamstrings work together to extend and flex the knee joint with each jump. These large muscle groups are heavily engaged during jump rope exercises, contributing to overall lower body strength and stability.Glutes
The glutes, or buttock muscles, act as stabilizers during jump rope exercise, helping to maintain proper alignment and absorb shock. They are essential for generating power and providing support throughout the movement. [caption id="attachment_627" align="aligncenter" width="300"]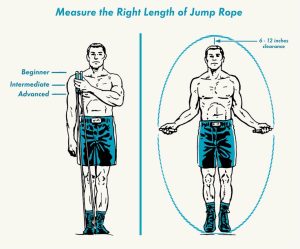 Muscles Targeted by Jump Rope Exercise[/caption]
Muscles Targeted by Jump Rope Exercise[/caption]
Core Muscles
Abdominals
The abdominal muscles play a crucial role in stabilizing the torso and maintaining proper posture during jump rope exercises. They contract to prevent excessive movement of the spine and pelvis, helping to protect against injury.Obliques
The oblique muscles, located on the sides of the abdomen, assist in rotational movements and lateral stability. They are activated during twisting motions and side-to-side jumps, helping to strengthen the core and improve balance.Upper Body Muscles
Shoulders and Arms
While the primary focus of jump rope exercise is on the lower body, the muscles of the upper body also play a supporting role. The shoulders and arms are involved in controlling the movement of the rope and generating momentum, contributing to overall coordination and endurance.Tips for Maximizing Muscle Engagement
To get the most out of your jump rope workout and target specific muscle groups effectively, consider the following tips:Proper Jumping Technique
Maintain good posture and keep your core engaged throughout the exercise. Land softly on the balls of your feet, and use your ankles, knees, and hips to absorb the impact.Variations in Jumping Styles
Experiment with different jumping styles, such as double unders, single-leg jumps, or high knees, to target various muscles and add variety to your workout routine.Incorporating Plyometrics
Incorporate plyometric exercises, such as jump squats or burpees, between jump rope intervals to increase intensity and further challenge your muscles.' [caption id="attachment_628" align="aligncenter" width="300"]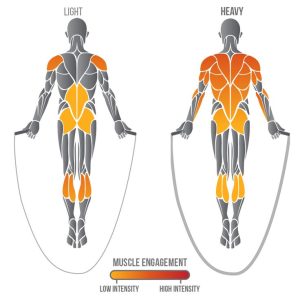 Tips for Maximizing Muscle Engagement[/caption]
Tips for Maximizing Muscle Engagement[/caption]
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While jump rope exercise is relatively simple, it's essential to avoid common mistakes that can compromise technique and effectiveness:- Using improper form: Avoid rounding your shoulders or arching your back excessively. Keep your chest up and your shoulders back to maintain proper alignment.
- Skipping warm-up: Always warm up before starting your jump rope workout to prepare your muscles and reduce the risk of injury.
- Overtraining: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your jump rope sessions to prevent overuse injuries and burnout.
